INTRODUCTION
The Bold Action to Strengthen Inclusive Care in Communities (BASIC) initiative aims to drive transformative change by ensuring that individuals with disabilities in Nigeria have equal access to high-quality healthcare, specifically focusing on Psychosocial Support (PSS) and Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights (SRHR), as well as socio-economic services. Through strategic collaborations and partnerships, the project is and will continue to advocate for the comprehensive enforcement of the disability act, with a particular emphasis on healthcare and social protection provisions for individuals with disabilities.
The primary goal is to enhance the accessibility and utilization of healthcare services among individuals with disabilities by addressing key barriers. Additionally, the project aims to create opportunities for sustainable socio-economic services within their communities. Special attention will be given to activities that deliver both immediate and long-term impacts. This includes engaging with health authorities to ensure that hospitals and healthcare facilities in the project locations provide reasonable accommodations for individuals with disabilities.
To achieve lasting results, the project is to prioritize capacity-building initiatives for healthcare providers, fostering disability-inclusive service delivery. By rebuilding trust and confidence in the health system, the initiative seeks to promote care-seeking behaviors among individuals with disabilities, particularly pregnant women, with the overarching goal of reducing mortality and morbidity related to pregnancy and childbirth.
Through community engagement efforts, the project is amplifying the voices and participation of individuals with disabilities, promoting equitable access to socio-economic and protection services. This will be boasted in the future by the establishment of Village Economic and Social Associations (VESA) and a robust community-based system designed to deliver effective Psychosocial Support (PSS) and Gender-Based Violence (GBV) services. The outcome of these efforts will not only be an improvement in the health of individuals with disabilities but also an elevation of their productivity and an enhancement of their socio-economic status.
This first year of intervention may not have provided all the necessary actions to accomplish these set goals but have laid a good foundation in achieving the overall objectives of this intervention through the engagement of relevant stakeholders, community dialogues, awareness campaigns, orientations and trainings.
The Objectives of the intervention for the year 2023
To contribute to the improvement of the quality of life of persons with disabilities and other vulnerable groups through the facilitation of community-based inclusive programs in Northern Nigeria’ with a specific objective to enhance the well-being of persons with disabilities and other vulnerable groups through improved access to affordable, right-based and sustainable basic packages of sexual and reproductive health and livelihood services,
ANNUAL NARRATIVE SUMMARY
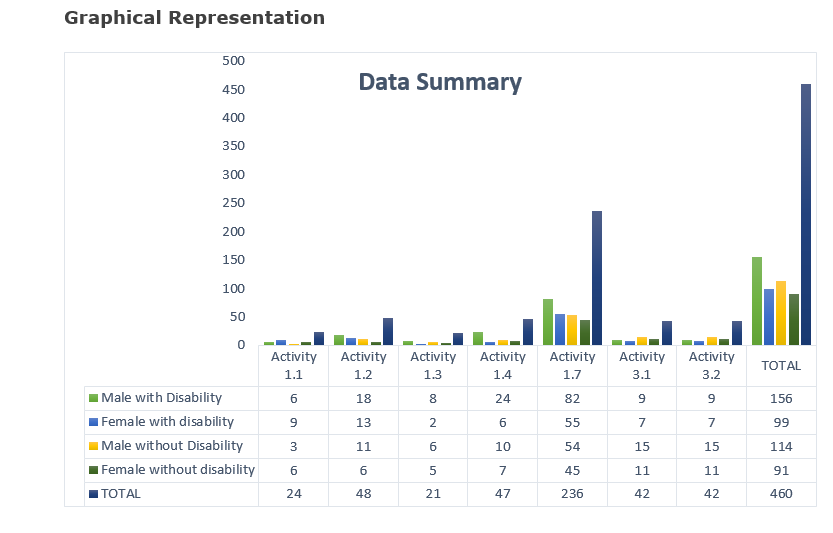
During the community entry process, our initiative focused on engaging a wide array of stakeholders, including state and local government ministries, departments, agencies, disability advocacy groups, healthcare providers, and community leaders. Communication media such as radio and television stations were also actively involved in supporting and enhancing effective disability inclusion in community activities. A total of 24 key stakeholders were visited to lay the foundation for our comprehensive campaign.
Service mapping was undertaken to facilitate referrals and collaboration among organizations in our implementation location, involving a total of 48 key stakeholders. Additionally, we invested in building the capacity of 42 individuals, who were subsequently engaged as Community-Based Volunteers. These volunteers played a crucial role in sensitizing the community on gender-based violence, and physical and sexual abuses against Persons with Disabilities (PWDs), and reporting such cases to LETSAI/CBM or making referrals through the established referral pathways. They were trained in Psychological First Aid (PFA) and Community-Based Psychosocial Support (CBPSS) to aid in the recovery and resilience of traumatized victims.
To increase awareness on disability rights and services, extensive awareness campaigns were conducted in the communities of Molai, Mafoni, and Kwana Yobe-Mashamari reaching a total number of 236 persons. These campaigns garnered massive turnout and a willingness to understand how best to ensure disability inclusion in community activities.
A radio and television program was organized to commemorate the International Day of Persons with Disability. Various sectors of PWDs spoke to the public about the support required by them in society, emphasizing the principle of “Nothing for them without them.” The program, aired on Borno Radio Television Corporation Maiduguri Channel 8, reached an estimated audience of 1,350,000 persons. Additionally, another radio program featuring informed panelists, including PWDs and advocates, addressed key concerns related to disability inclusion, reaching an estimated audience of 39,511 persons.
PLANNED ACTIVITIES AND RESULTS ACHIEVED
Activity 1.1 conduct community entry with all stakeholders including state and local government ministries, departments and agencies, CSOS OPDS, women and youth-led organizations
We carried out Successful Community Entry establishing strong partnerships, effective communication, and inclusive decision-making processes. This comprehensive understanding of community needs provides a solid foundation for impactful interventions, fostering ongoing collaboration and engagement for program success.
The following stakeholders were met; community leaders (Bulamas, Lawans, Religious leaders), government agencies (Government Health care facility management, Ministries of Women affairs and Social Development, Borno State Primary Health Care Development Agency (PHCDA), Borno State Universal Basic Education Board (SUBEB), Borno State Ministry of Agriculture and Borno State Health Insurance Scheme) Disability advocacy groups like the Joint Association of Persons with Disability (JONAPD), healthcare providers and education institutions identified in the localities.
Lesson learnt
Inclusive partnerships: Engaging diverse stakeholders, including government agencies, CSOs, OPDs, and women and youth-led organizations, creates a powerful platform for addressing community needs and driving sustainable development. Collaboration among stakeholders with different perspectives and expertise leads to more comprehensive and effective solutions.
Participation and ownership: Encouraging active participation from community members fosters a sense of ownership and accountability. Meaningful involvement of marginalized groups ensures that their voices are heard, and their needs are adequately addressed.
Capacity building: Investing in capacity building initiatives for all stakeholders is crucial for sustainable development. Providing training and resources to government officials, CSOs, OPDs, and women and youth-led organizations strengthens their ability to contribute effectively to community development initiatives.
Continuous communication: Establishing open and transparent communication channels among stakeholders is essential for maintaining collaboration and synergy. Regular dialogue and information sharing help build trust, align goals, and resolve conflicts, if any.
Adaptability and flexibility: Communities are dynamic entities, and their needs and priorities may evolve over time. It is essential to remain adaptable and flexible in responding to changing circumstances and adjusting strategies accordingly.
Activity 1.2: Community Mapping for Resources and Structures
Through mapping, valuable insights were gained by identifying community resources and structures, including Community Development Committee (CDC) and Organisation of persons with disabilities (OPDs,) lay the foundation for future collaborations, emphasizing leveraging existing resources. Identification of collaboration opportunities with external organizations was facilitated through a participatory approach involving community members in interviews, surveys, and group discussions.
The mapping was carried out in Mafoni, Molai in MMC Local Government area and Mashamari-Kwana yobe in Jere Local Government area other organisations provide services like managing GBV cases where identified in Mashamari-Kwana yobe we have Internationala Rescue Committee (IRC) and Molai community we have Save the Children.
During the mapping exercise we also identified the various community leaders such as the Bulamas and the number per community, the Lawans and the religious leaders of those communities.
Lesson learnt
The community mapping activity provided valuable lessons that can inform future development initiatives. Firstly, community engagement is a critical aspect of any mapping exercise. Actively involving community members throughout the process fosters ownership, trust, and a sense of empowerment. By encouraging participation from diverse perspectives, we were able to capture a more comprehensive picture of the community’s resources and needs.
Secondly, the mapping process highlighted the significance of collaboration and partnership. Working closely with existing structures like the Community Development Committees and Other People’s Development organizations enabled us to leverage their expertise, networks, and resources effectively. This collaboration helped to maximize the impact of our interventions and ensured sustainability beyond the project’s duration.
Lastly, addressing the challenges of limited participation and resource disparities underscored the need for a holistic approach to community development. It is essential to identify and address the underlying factors that contribute to unequal access to resources. This may involve advocating for policy changes, mobilizing external support, and implementing long-term strategies to uplift marginalized communities.
Activity 3.1 Strengthen/establish community-based mechanisms (CBM) to provide local psychosocial and GBV Case management assistance
A community based mechanism was established through the selection of volunteers across the communities, inclusive of Organisation of Persons with Disabilities (OPDs), Youth Group, Women Group, JONAPWD and Health Workers. A total number of 42 persons from the 3 communities and 14 per community.
Activity 3.2: Training of Community Volunteers on PSS and GBV Case Management
A 3-day training was conducted for some selected beneficiaries from the community inclusive of Organisation of Persons with Disabilities (OPDs) Organization of Persons with Disabilities (OPDs), Youth Group, Women Group, JONAPWD and Health Workers to ensure increased awareness and understanding of GBV, equipping participants with skills to recognize, respond, and support GBV survivors.
Participants were selected from across the three communities of intervention, Molai, Mafoni and Mashamari and at the end of the training the following were achieved;
-
- Knowledge Improvement: Participants demonstrated a better understanding of GBV, its different forms, and how to recognize and respond to it, by this the training have achieved its knowledge improvement target.
-
- Behavior Change: Participants exhibited positive changes in attitudes and behaviors related to gender-based violence, such as challenging harmful norms or supporting survivors, this was also considered a successful outcome.
-
- Enhanced Support Services: The training aimed to improve the quality and accessibility of support services for survivors of GBV, achieving this target was significant accomplishment. As participants can now identify cases and make necessary referrals.
During the training, participants were also schooled on Psychological first aid and community-based psychosocial support. At the end of the training, the community volunteers demonstrated a strong understanding of Psychological First Aid and community-based psychosocial support. They could identify signs of distress in individuals and felt confident in applying the principles of PFA to offer immediate support.
Some key achievements include:
-
- Improved knowledge of effective communication techniques and active listening skills.
-
- Enhanced capacity to recognize and address cultural considerations when providing support.
-
- Increased awareness of self-care practices to prevent burnout and compassion fatigue.
-
- Establishment of a cohesive group of volunteers committed to supporting each other and the community.
The participants also underwent a training on empowering community volunteers for effective data collection and monitoring in community projects (MEAL) The training achieved significant accomplishments by empowering community volunteers with knowledge and skills to gather reliable data and contribute effectively to community-based projects.
Activity 1.7a: Quarterly Community Outreaches for Awareness
The quarterly community outreach was focused on raising awareness and promoting sensitization on disability rights and related issues. In addition to disability rights, we address Gender-Based Violence (GBV) and Protection from Sexual Exploitation and Abuse (PSEA). The overarching goal created a more inclusive community for persons with disabilities, providing psychosocial support, amplifying the voices of survivors of gender-based violence, and enhancing community awareness on disability rights, accesses to services and absolute community inclusion. The initiative also educates on response and mitigation strategies, policies, and ways men can support women and girls in accessing gender-based violence services for persons with disabilities and other community members.
This activity was carried out targeting Molai Community members, Kwanan Yobe (Masamari Ward) community members, Mafoni Kalwa community members, Community Health workers, JONAPWD and the Community leaders.
Key findings
Little Awareness on Disability Rights: The community exhibited minimal awareness of the rights of Persons with disabilities. Through this awareness exercise, community members gained knowledge about the rights of individuals with disabilities, fostering better support and integration in society
Cultural Sensitivity: The initiative emphasized the importance of cultural sensitivity in disability awareness initiatives, highlighting the effectiveness of culturally appropriate messaging and activities within the community where the Persons with Disabilities with not be stigmatized.
Collaboration and Partnerships: Strengthened collaborations and partnerships between community organizations, local government bodies, and advocacy groups were observed, creating a supportive network for disability rights.
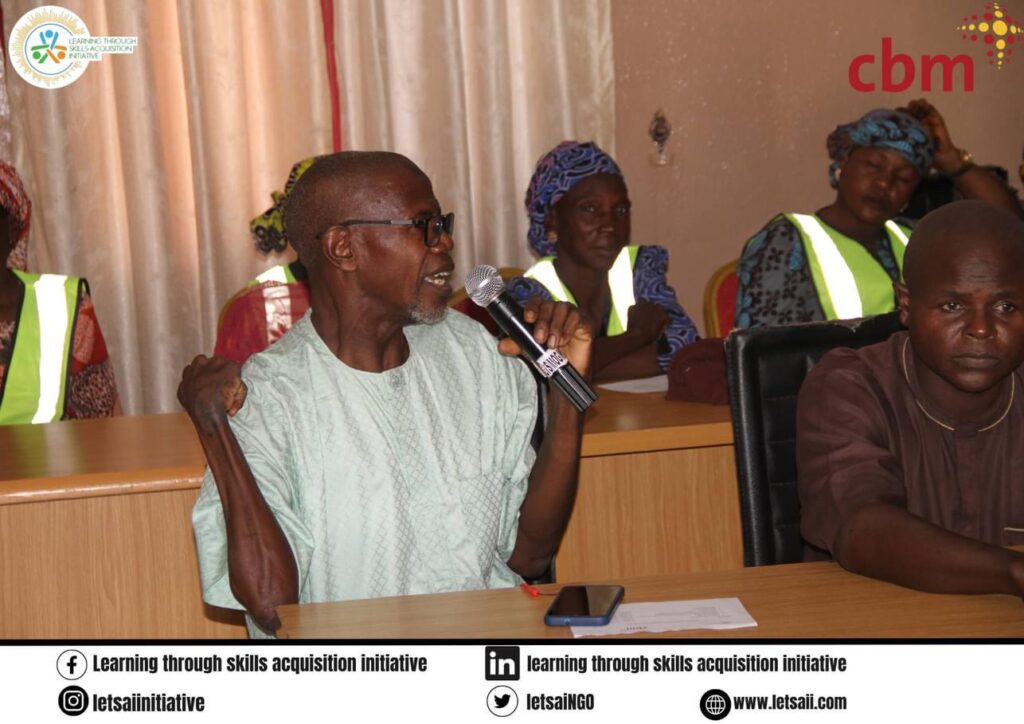
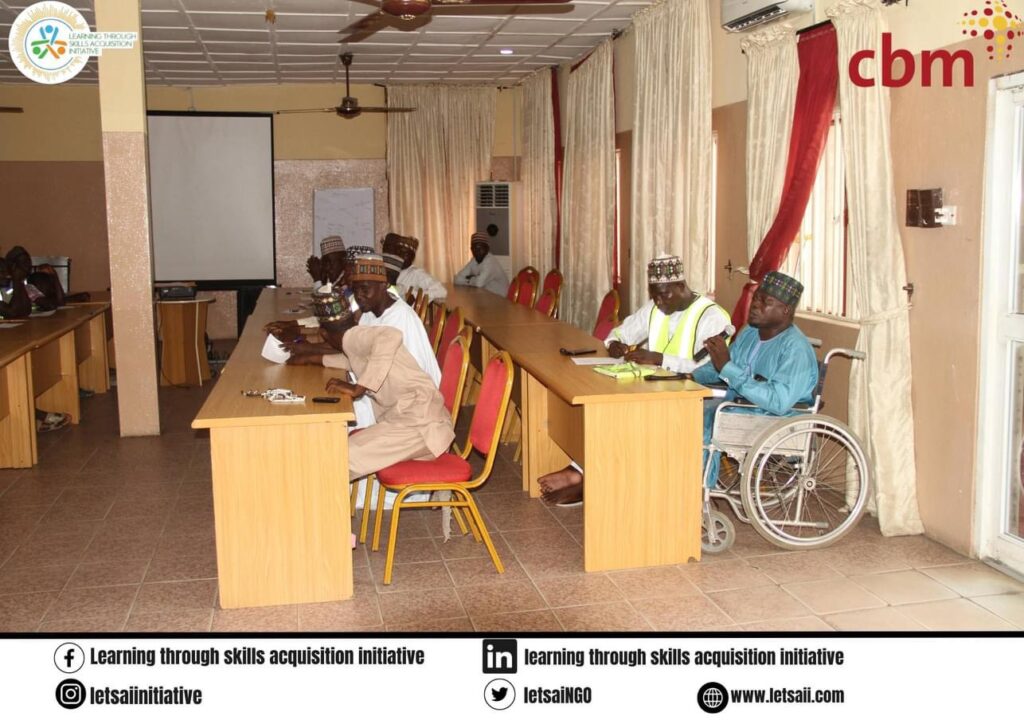
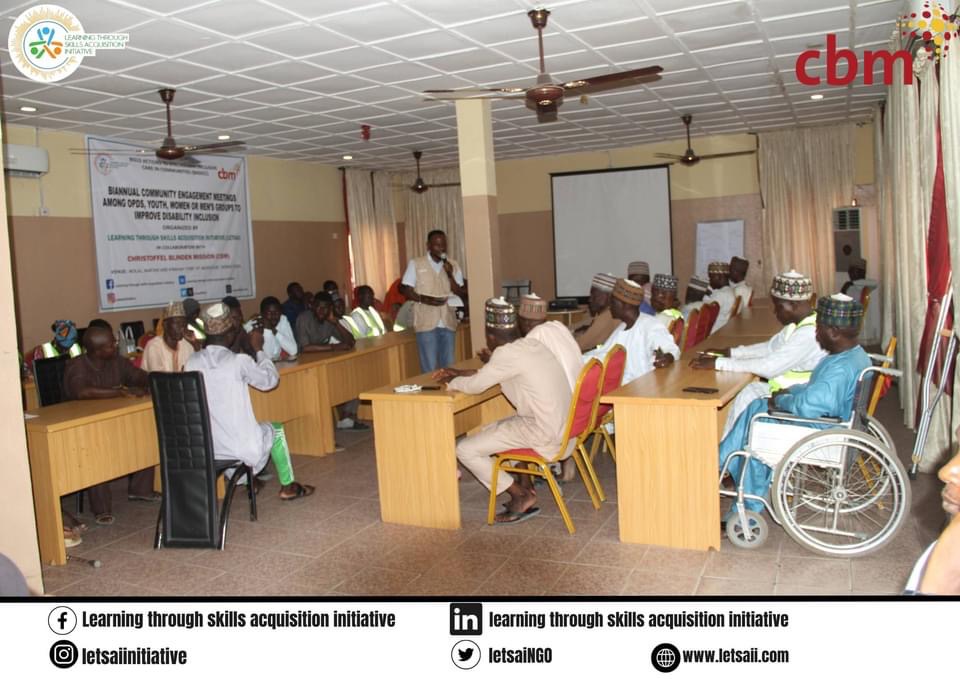
Activity 1.4: Biannual Community Engagement Meetings
Biannual meetings enhanced disability inclusion by fostering collaboration and resolving challenges faced by persons with disabilities. A participatory approach involving diverse stakeholders like the Organization of Persons with Disabilities (OPDs), youth, women, men’s groups, and various community leaders (Religious and Traditional). At the end of this meeting we came up with an action plan to collaboratively ensures tangible changes in community dynamics. This action plan was developed by all the participants of which will enhance equal access for persons with disability, disability inclusive projects, with all the stakeholders pledging to be advocates of disability inclusion. The overreaching goal is to further enhance awareness and inclusiveness within the communities.
Lesson Learnt
Promoting Inclusive Partnerships: Inclusive partnerships form the cornerstone of effective community development. The engagement of diverse stakeholders, ranging from government agencies and civil society organizations (CSOs) to organizations representing persons with disabilities (OPDs) and those led by women and youth, creates a dynamic platform for addressing community needs and steering sustainable development efforts. The collaboration of stakeholders with varied perspectives and expertise significantly enhances the formulation and implementation of comprehensive solutions.
Encouraging Participation and Ownership: Active involvement of community members is pivotal in fostering a sense of ownership and accountability within the community. Actively engaging marginalized groups ensures that their voices are not only heard but also given due consideration in the decision-making processes. This approach facilitates more inclusive and tailored solutions that address the specific needs of diverse segments of the community.
Facilitating Continuous Communication: The establishment of open and transparent communication channels among stakeholders is indispensable for the continuity of collaboration and synergy. Regular dialogue and information sharing play a crucial role in building trust, aligning goals, and resolving conflicts that may arise. By fostering a culture of ongoing communication, a robust foundation is laid for sustained partnerships and collective action.
Activity 1.3: 3-day Training on CBID for OPDs and Stakeholders
The training in Maiduguri aimed to go beyond mere awareness and actively enhance the knowledge and capacity of Organizations of Persons with Disabilities (OPDs) and community stakeholders. As part of the Bold Actions in Strengthening Care in Communities (BASICC) Project, the training focused on promoting the principles of Community-Based Inclusive Development (CBID) and empowering participants to actively engage in inclusive practices within their communities.
Participants were drawn from across the communities comprising of community volunteers, social welfare workers, OPDs, community health workers and traditional leaders. LETSAI staff also benefited from the training as the training was been conducted by CBM Maiduguri.
Lesson learned
Investing in Capacity Building: Investing in capacity building emerges as a pivotal strategy for fostering sustainable development within communities. The significance of this investment becomes evident when targeted training and resources are provided to Civil Society Organizations (CSOs), Organizations of Persons with Disabilities (OPDs), and groups led by women and youth. This strategic approach not only enhances their skills and knowledge but also empowers them to make meaningful contributions to community development initiatives.
Transformative Impact: The transformative impact of capacity building initiatives was underscored by a stakeholder who highlighted a newfound proficiency in using more inclusive language when interacting with Persons with Disabilities (PWDs). This revelation emphasizes that capacity building goes beyond mere skill acquisition; it plays a crucial role in reshaping attitudes and fostering a more inclusive community.
Inclusive Project Development: One of the key takeaways from the training sessions was the emphasis on inclusive project development. Participants learned how to design and implement community development projects that are accessible to everyone, regardless of their abilities. This approach ensures that the benefits of development initiatives reach all members of the community, promoting equality and social inclusion.
Effective Communication Strategies: The training sessions delved into effective communication strategies with Persons with Disabilities. Participants gained insights into fostering friendly and inclusive communication without stigmatizing individuals with disabilities. They also acquired knowledge about the appropriate use of language and words, avoiding those that may perpetuate stereotypes or create barriers when interacting with persons with disabilities.
Understanding Legal Frameworks: Participants were equipped with a comprehensive understanding of the legislations that support disability inclusion. This knowledge not only extends to local laws in Borno State, Nigeria, but also encompasses global perspectives. By being aware of the legal backing for persons with disabilities, community members can advocate for and uphold the rights of individuals with disabilities, contributing to a more just and equitable society.
Empowering Communities: In summary, the investment in capacity building has proven to be a catalyst for empowering communities. Beyond skill development, it has fostered inclusive project development, improved communication, and enhanced awareness of legal frameworks supporting disability inclusion. The lessons learned from this initiative lay a solid foundation for building more resilient, equitable, and inclusive communities in Borno State and beyond
Activity 1.7b: Commemoration of International Day of Persons with Disabilities
The observance of the International Day of Persons with Disabilities serves as a significant platform for raising awareness and fostering stakeholder engagement regarding the imperative of disability inclusion. This occasion not only provides an opportunity for individuals with disabilities to showcase their talents but also facilitates an avenue for them to articulate their concerns regarding the challenges they encounter within the community.
The impact of this commemoration extends beyond the immediate event, as various radio and television programs dedicated to persons with disabilities contribute to heightened awareness of their rights. These broadcasts not only empower individuals with disabilities by informing them of their entitlements but also play a crucial role in educating the general public about the importance of integrating disability inclusion into various community activities. As a result, the International Day of Persons with Disabilities becomes a catalyst for positive change, fostering a more informed and inclusive society
The objective of commemorating the International Day of Persons with Disabilities is to foster an understanding of disability issues and mobilize support for the dignity, rights, and well-being of individuals with disabilities.
We were able to collaborate with Persons with Disabilities to identify areas where support is needed for the commemoration wherein we supported in the area of media coverage and also engaged two (2) sign language interpretation. We further organized a pre-recorded panel discussion on Disability inclusion where four (4) panelists were engaged in both Hausa and Kanuri Language and they discussed, what disability entails, the disabilities prevalent in Borno State, how to ensure disability inclusion and the advice for the government and the public on disability inclusion where a lot of good messages on disability inclusion were passed to the public. This radio session was aired few days after the commemoration of persons with disabilities and its reached beneficiaries is estimated to be 1,389,511 (There are documents to back this claim)
Commemoration Day
The International Day for the commemoration of persons with disability is originally the 3rd of December which happens to be on Sunday for this year 2023. To ensure full participation and necessary convenience for persons with disability, The Network of Persons with Disabilities in Borno State marked hers on the 11th of December 2023. And LETSAI participated fully through Media support and inclusive communication.
Media Coverage: BRTV was engaged for amplify media coverage through television and radio mediums for publicity, awareness, and orientation.
Targets: The target includes, Community Health Workers, JONAPWD, Community leaders, The Government, and the General Public
PLANNED ACTIVITIES FOR YEAR 2024
| Result 1: Communities are empowered on Disability inclusion using CBID strategies |
| Activity 1.4: Conduct biannual community engagement meetings among identified OPDs, youth, women or men’s groups to improve disability inclusion in the community |
| Activity 1.5: Work with JONAPWD, OPDs and other networks on advocacy for state Disability ACT/ implementation for persons with disabilities. |
| Activity 1.6: Conduct 3-day technical consultative meeting for the Development and production of Information Education and Communication (IEC) materials for community awareness raising |
| Activity 1.7: Conduct quarterly community outreaches for awareness and sensitization on Disability rights and other related issues |
| Activity 1.8: Accessibility audit in selected health facilities for improved service delivery. |
| Activity 1.9: Construct ramps, Handrails and other recommended physical infrastructure for access improvement for persons with disability |
| Activity 1.10: Commemorate the International Day of Persons with disabilities (every December 3rd) |
| Result 2: Improved access to sustainable livelihood for persons with disability and other vulnerable groups. |
| Activity 2.1:Formation and Training of Village Economic and Social Association in the target communities |
| Activity 2.2:Procurement and Distribution of VESA Materials |
| Activity 2.3:Training of target groups on IGA and business skills |
| Activity 2.4: Enrolment of target groups into identified skills acquisition centers |
| Activity 2.5:Provision of start-up grants for business target groups and trainee from skill acquisition scheme |
| Result 3: Improved access to services at the community level including health facilities |
| Activity 3.3:Distribution of dignity kit to support Women and Girls with disabilities in menstrual Hygiene management |
| Activity 3.4: Pay premium for targeted persons with disabilities and other vulnerable groups in the informal sector on the State Health Insurance Scheme in the targeted states. |
| Activity 3.5:Procurement and distribution of Assistive devices |
CHALLENGES
-
- Despite the overall success of the project implementation, several challenges were encountered throughout the process. One notable challenge was ensuring the equal participation of all stakeholders. It was crucial to create an inclusive and safe space where marginalized groups, such as persons with disabilities, women, and youth, felt comfortable sharing their views. Efforts were made to address any power imbalances and ensure that their voices were heard and valued.
-
- Another challenge related to coordination and communication among stakeholders. Given the diverse range of participants, coordinating schedules, aligning priorities, and maintaining ongoing engagement required careful planning and clear communication channels. Regular updates and reminders were necessary to keep everyone informed and involved in the process.
-
- One of the primary challenges during community mapping was limited participation from certain segments of the community. Some individuals were hesitant to engage, potentially due to distrust, apathy, or previous negative experiences. Overcoming this challenge required building rapport, fostering trust, and emphasizing the inclusive nature of the mapping exercise.
-
- Another challenge was the scarcity of resources in certain areas. While the community possessed numerous strengths, it became evident that some marginalized regions faced significant gaps in infrastructure, education, and healthcare facilities. Addressing these disparities would require targeted interventions and the mobilization of additional resources beyond the community’s immediate capacity
-
- Economic Challenges in Nigeria: Economic conditions in Nigeria, including escalating costs and the decrease in the value of the Naira, have adversely affected project implementation. An urgent upward review of the budget is necessary to navigate economic challenges. This will allow the project to adapt to the changing economic landscape, ensuring continued success and sustainability in the face of financial uncertainties.
ACTIVITY PICTURES



